Extreme rainfall induced risk mapping for metro transit systems: Shanghai metro network as a case
文章作者(*為通訊):
1. Dongming Zhang?1,3,*
2. Hao Bai?1,3
3. Canzheng Zheng?5
4. Hongwei Huang?1,3
5. Bilal M. Ayyub?2,3,4
6. Wenjun Cao?6
作者單位:
1.Key Laboratory of Geotechnical and Underground Engineering of Minister of Education and Department of Geotechnical Engineering, Tongii University, Shanghai 200092, China
2.Center for Technology and Systems Management, Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, University of Maryland, College Park, MD,20742, USA
3.International Joint Research Center for Resilient Infrastructure, Tongji University, China
4.Applied Economics Office, National Institute of Standards and Technology, Department of Commerce, USA
5.Jinan Rail Transit Group Co., Ltd, Jinan, China
6.Department of Civil Engineering, the University of Hong Kong, Hong Kong, China
關(guān)鍵詞:
Risk assessment; Metro flooding; Extreme rainfall; Multi-layer network; Resilience.
原文鏈接:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2025.111234
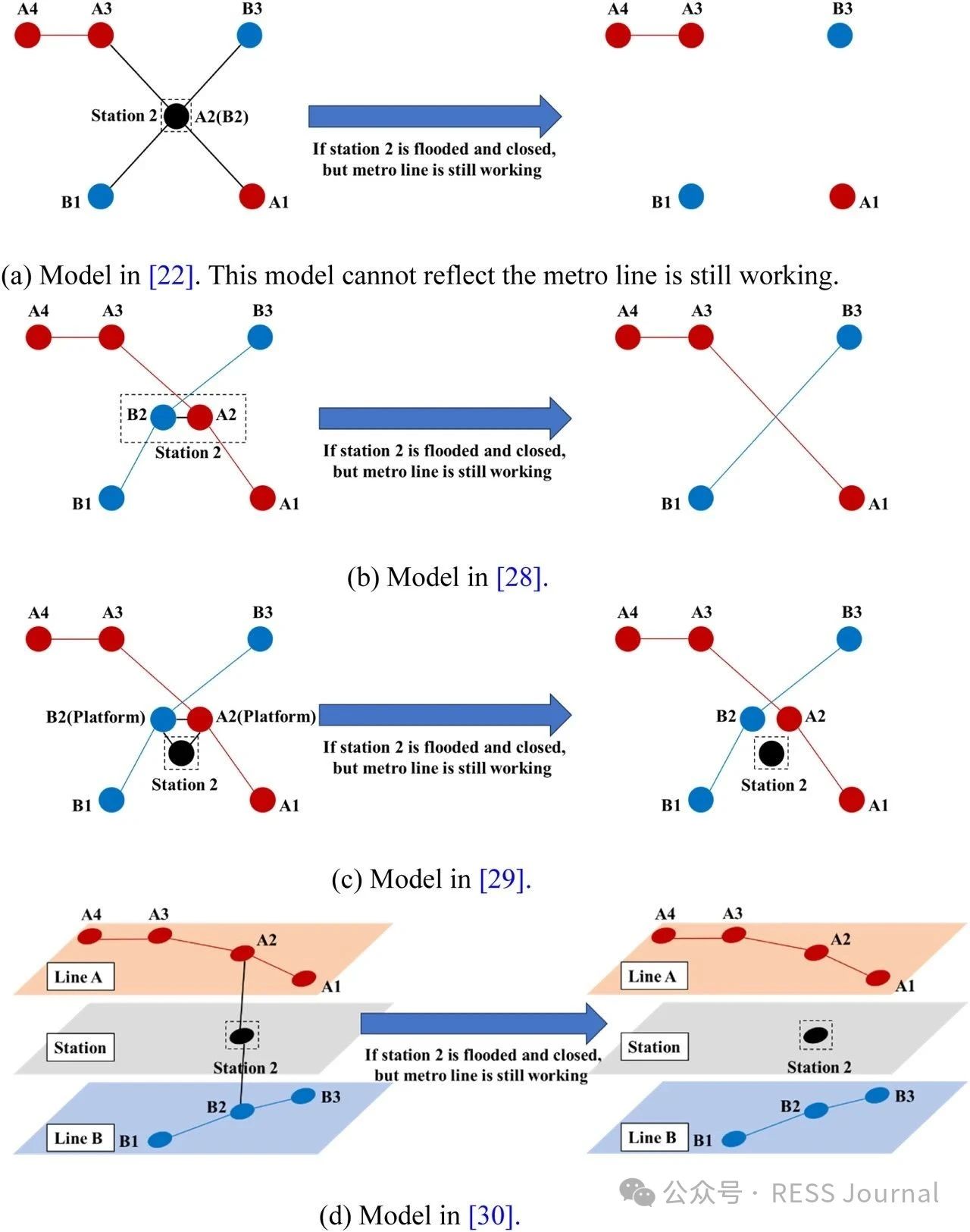
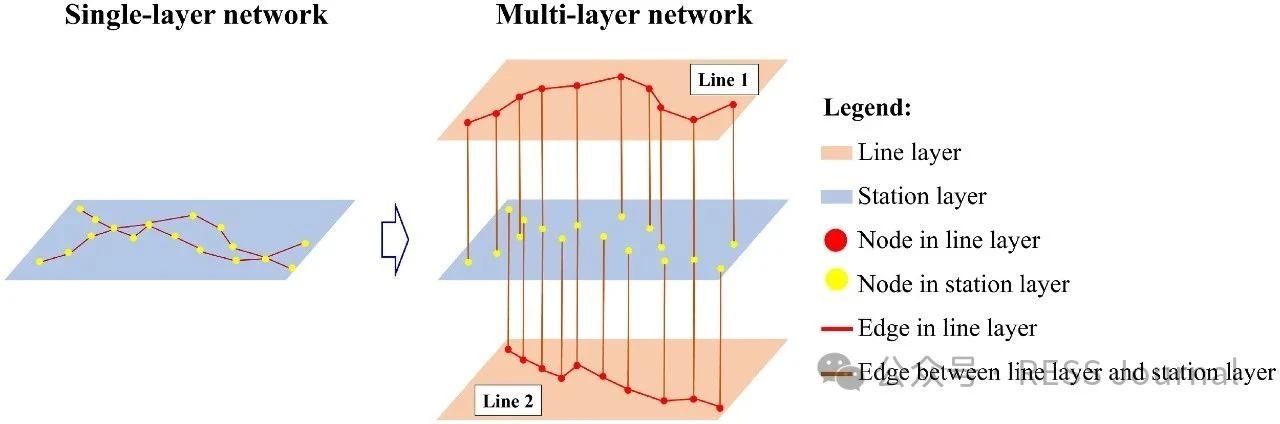
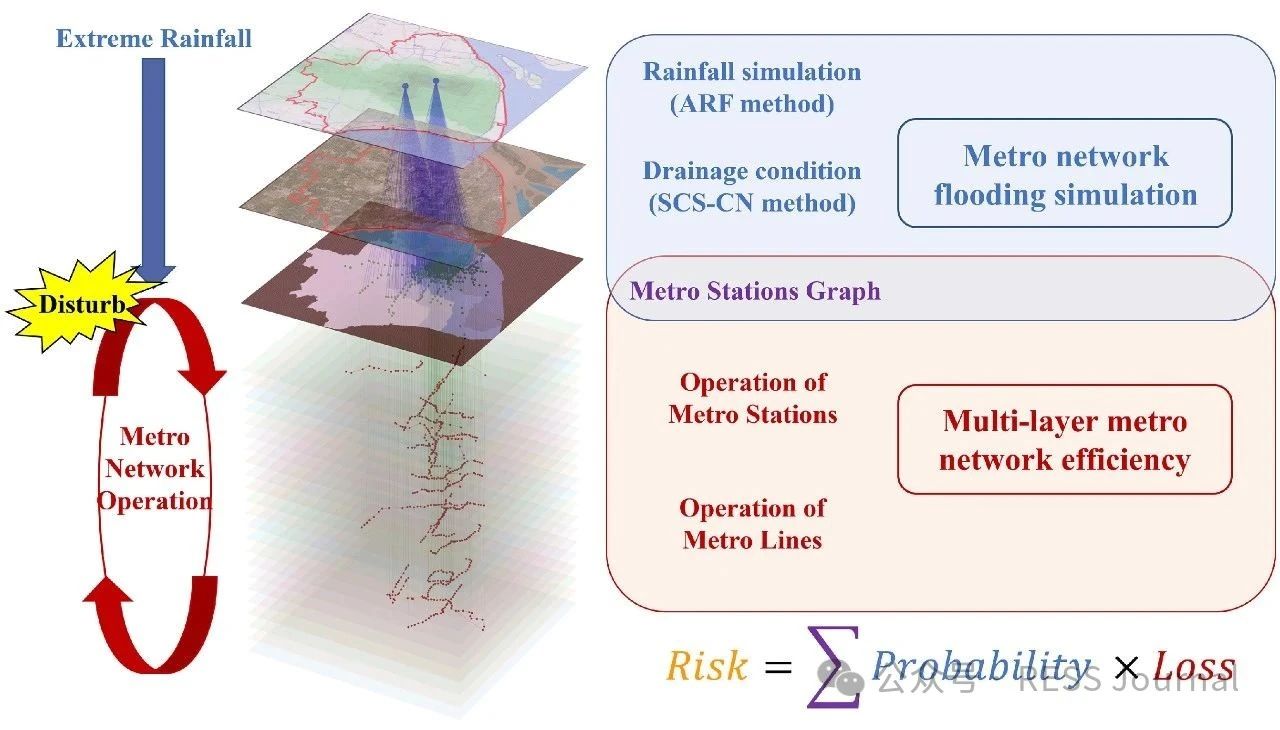
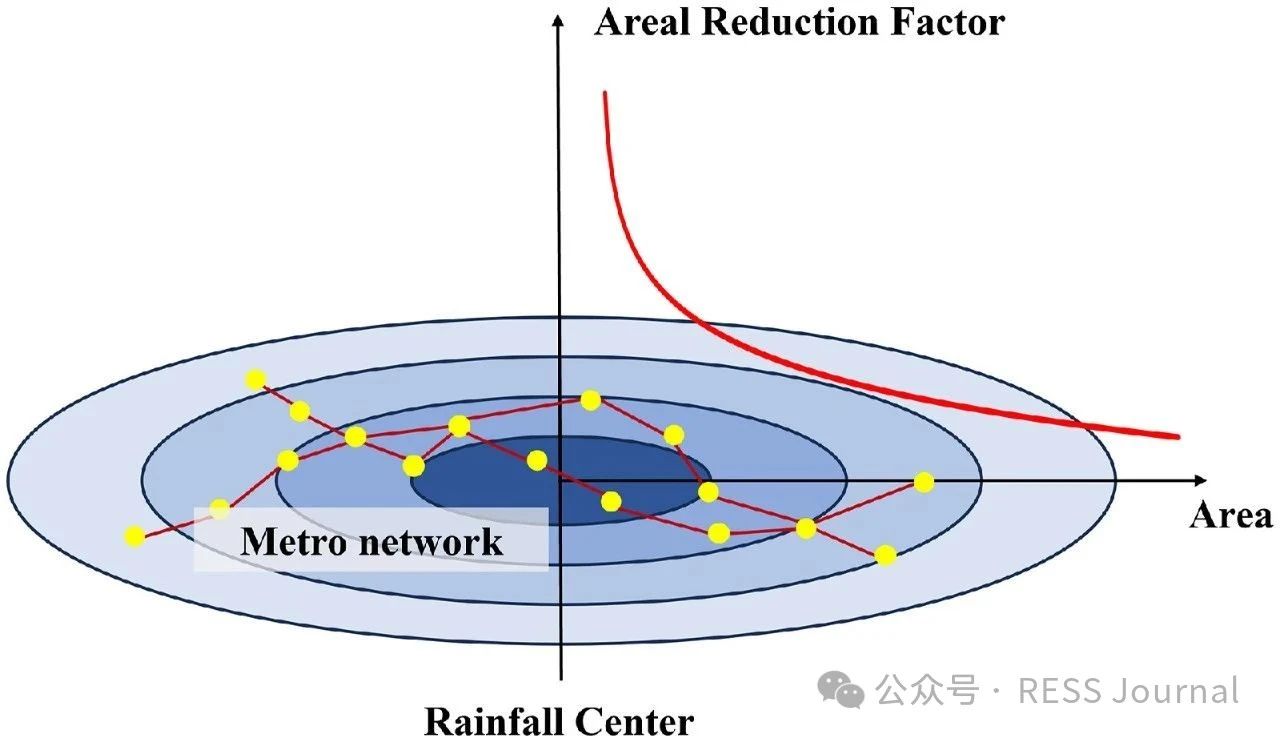
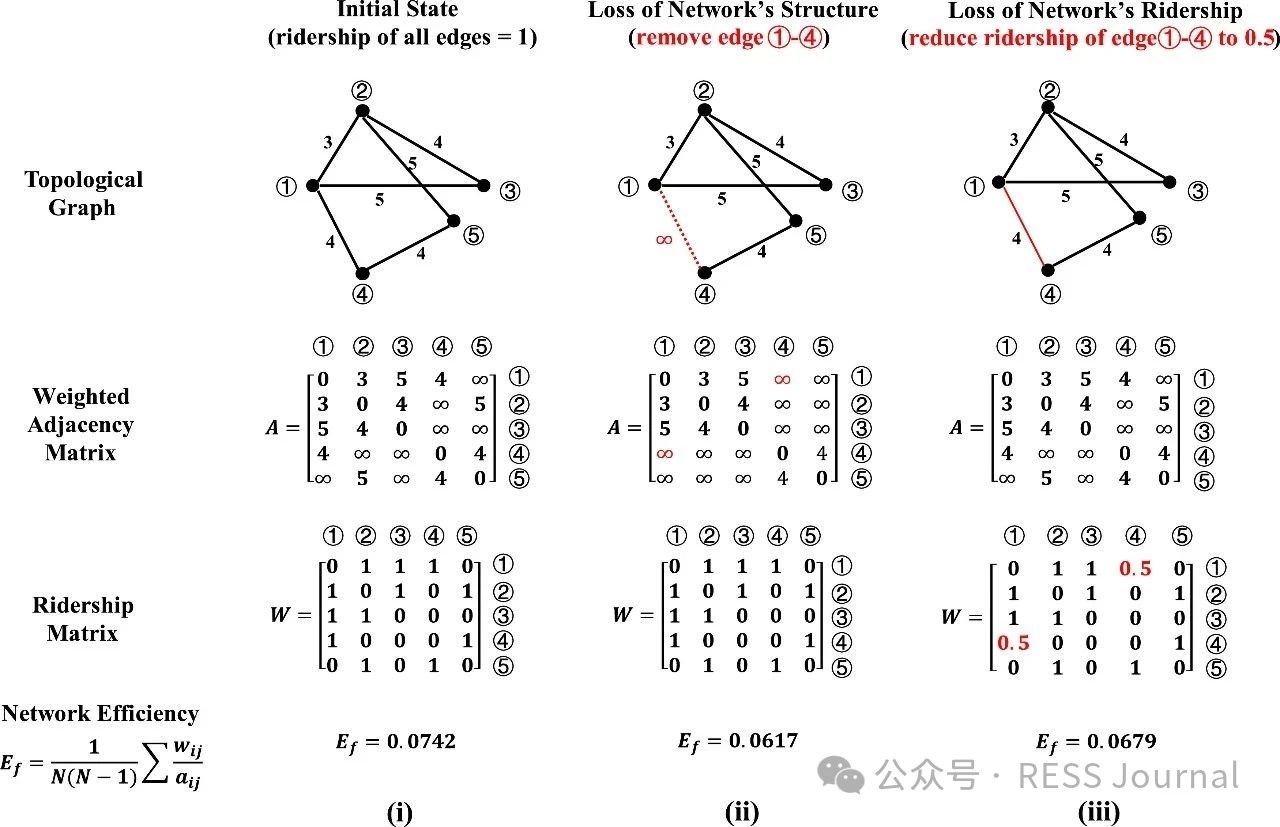
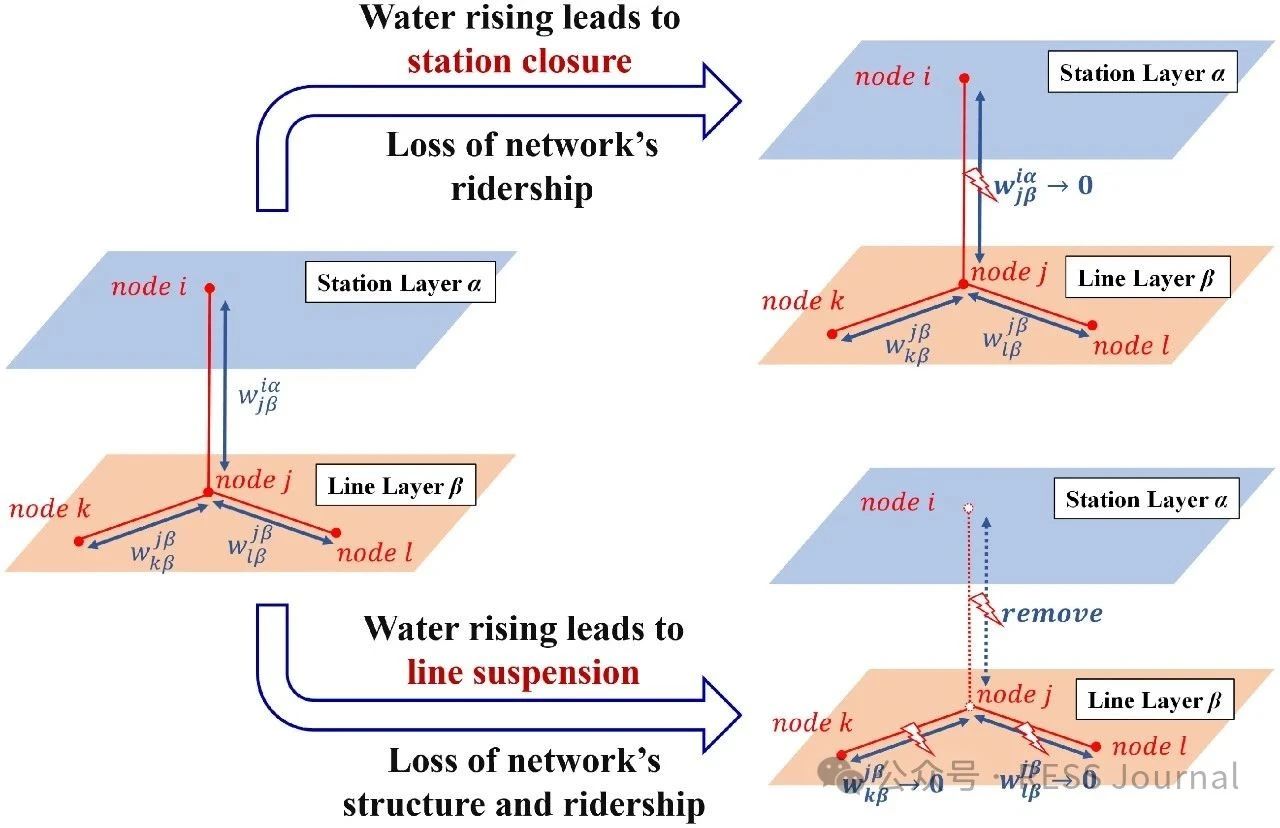

In recent years, a changing climate has induced flood risk as a great threat to the safety and reliability of the metro transit network in mega-cities. A highly networked metro system can lead to a quick spread of this risk, and furthermore, the impact range of single-node accidents of a network is nonlinearly amplified through network connectedness defined by its topology. This study proposes a risk assessment framework integrating extreme rainfall simulation and network loss analysis. The methodology employs the Areal Reduction Factor (ARF) and Soil Conservation Service Curve Number (SCS-CN) to model rainfall-induced flooding, coupled with a multi-layer network-based approach that distinguishes topological interactions between stations and lines. Taking Shanghai metro as an example, this paper highlights its risk follows an exponential distribution to extreme rainfall events, characterized by the finding that nearly 50 % of extreme rainfall events result in <5 % network loss, whereas fewer than 5 % of the events lead to >50 % network loss. When rainfall centers are located in the urban center where metro stations are densely distributed and intricately connected, or when the rainfall intensity and the spatial distribution uncertainty increases, it will pose a greater risk to the metro network.
相關(guān)推薦:軌道交通展展位預訂??軌道交通展免費報名參觀


6月20日,第四代吉利醇氫電動轎車交車儀式在張家口市民廣場舉行,首批36輛醇氫電動轎車正式交付,主要應用于當?shù)爻鲎廛囆袠I(yè)。據(jù)了解,張家口市大力鼓勵出租車經(jīng)營者自愿更換電動出租車。目前,全市電動出租車保有量達1137輛,位居全省前列。 近年來,張家口市鞏固國家公交都市建設示范城市創(chuàng)建成果,加快構(gòu)建綠色交通體系,推進新能源在城市公交、出租車和配送領(lǐng)域的推廣使用,不斷優(yōu)化城市綠色出行環(huán)境,推動交通結(jié)構(gòu)綠色低碳轉(zhuǎn)型。 筆者在張家口市橋西區(qū)展覽館公交站看到,一輛輛車牌上印有“F”標識的氫燃料電池公交車從身邊駛過,成為一道亮麗風景線。“目前,全市擁有綠色能源公交車2050輛,占公交車輛總數(shù)的90.4%,主城區(qū)綠色能源公交車輛占比100%。”張家口市交通運輸局相關(guān)負責人介紹,該市已投運氫燃料電池公交車444輛,位居全國首位。 該市不斷豐富氫能交通應用場景,氫燃料電池重卡已應用于當?shù)孛禾窟\輸服務以及建筑垃圾倒運領(lǐng)域。目前,該市有氫燃料電池提供動力的物流車725輛、牽引車3輛、倉柵車40輛。“動力系統(tǒng)由本地企業(yè)生產(chǎn)制造,具有快速加氫、功率高、續(xù)航里程長等優(yōu)勢。”張家口億華通動力科技有限公司品牌部負責人李靖介紹,氫燃料電池重卡每加滿一次燃料...